Free your Mac039s IP
The internet has become as much a part of OS X as Mail.app. But if your like me, your mac is stuck behind several layers of security. My first layer of “protection” is Comcast. Comcast really does not want you running your own server with their cable system. They effectively block IMAP ports to prevent you from running your mac as a mail server. They have even begun to packet shape BitTorrent traffic. There is little the average user can do about this. This outline is about the other layers of security that prevent you from using VNC, Devonthink Server, Omnifocus server and many other applications that now offer data up over the internet. I’ve tailored it for use with the Airport Extreme base station
The first step is to get a static DNS entry and point it at your router. I use DynDNS. I chose something memorable so I don’t have to look it up all the time. If you can remember the IP address of your router, then you can probably skip this step.
Open up the Airport Utility and select your router. Click the “Manual” button in the lower left corner. The IP address that your provider has assigned to the router should appear at the bottom of the next screen. Write that down.
Now go back to the DynDNS web page and enter your routers IP address as the address that you would like traffic routed to. You’re telling DynDNS to make a readable URL address available and point all traffic to your router. Don’t worry, there are TWO firewalls between the internet and your Mac.
Get a static IP address for your Mac
Your Mac’s IP address can be found in the System Preferences. Open the “Network” preferences and select whatever connection you use to get on the internet. Mine is Ethernet 1. On the TCP/IP lozenge, choose “Using DHCP with manual address” as the method for “Configure IPv4”. Most likely, your router is distributing a series of IP address from 10.0.1.1 to 10.0.1.200. You need to choose an IP address outside this range. I suggest using 10.0.1.201. Type that into the box next to “IP Address”. The “Subnet Mask” and “Router” IP address should already be set. Set the DNS server to your router as shown. We only need the router to do the DNS look-up for us anyway.
 Firewalls
Firewalls
The Airport Extreme is your first line of protection. No unsolicited traffic can make it past the router. That is, unless we tell the router to make some openings in the firewall. These are called Port forwarding or Port Mapping. To add port mapping to the Airport, click the “Advanced” button at the top of the Airport Utility window.
Now click the “Port Mapping” lozenge
 Click the little plus sign underneath the “Allow:” box. The next pop-up window allows you to either choose a common service to add such as Apple Remote Desktop or Windows Sharing. A really useful port to open is the one used for VNC. This will allow you to control your mac remotely from anywhere on the internet.
Click the little plus sign underneath the “Allow:” box. The next pop-up window allows you to either choose a common service to add such as Apple Remote Desktop or Windows Sharing. A really useful port to open is the one used for VNC. This will allow you to control your mac remotely from anywhere on the internet.

To add a VNC port, do not select a service. We are going to create one instead. VNC typically uses port 5901, so type that into all the port boxes shown. Enter your Mac’s IP address as the destination of the ports forwarding. This essentially tells the router to send any traffic it receives on port 5901 directly to your Mac.

So now the router understands what to do with the traffic. You have to tell your Mac what to do with it. I said earlier that there were TWO firewalls. The first is the Airport Extreme. The second is the one built into your Mac. Back to the system preferences and open the “Sharing” preferences. Click the “Firewall” lozenge. If you have never done so, turn on your Mac’s firewall and then flog yourself for not maintaining your personal security. Never do that again!
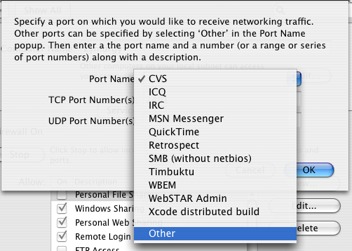
 Now click the “New” button to open up a new connection through the Macs firewall. From the pull down menu, select “Other” and enter 5901 as the port number to allow through.
Now click the “New” button to open up a new connection through the Macs firewall. From the pull down menu, select “Other” and enter 5901 as the port number to allow through.
 Now the world can access port 5901 on your Mac. That’s kind of scary. You can always go into either Airport Utility or the Mac Firewall and turn off the port again without deleting all the work you did. The same technique can be used to open up BitTorrent or Telekinesis ports. There are several online tools that will tell you if the ports have been successfully unblocked.
Now the world can access port 5901 on your Mac. That’s kind of scary. You can always go into either Airport Utility or the Mac Firewall and turn off the port again without deleting all the work you did. The same technique can be used to open up BitTorrent or Telekinesis ports. There are several online tools that will tell you if the ports have been successfully unblocked.
